5 Tips for Faster CAN Bus Diagnostics
5 Tips for Faster CAN Bus Diagnostics
5 Essential Tips for Successful CAN Bus Diagnostics
IF YOU are new to the world of CAN Bus diagnostics, you're in the right place. CAN Bus can be tricky to diagnose, but by following these five steps, you can make the process much easier. As someone experienced in CAN Bus diagnostics, I understand the challenges, and I'm here to help you navigate through them.

Tip 1: Perform a Function Test
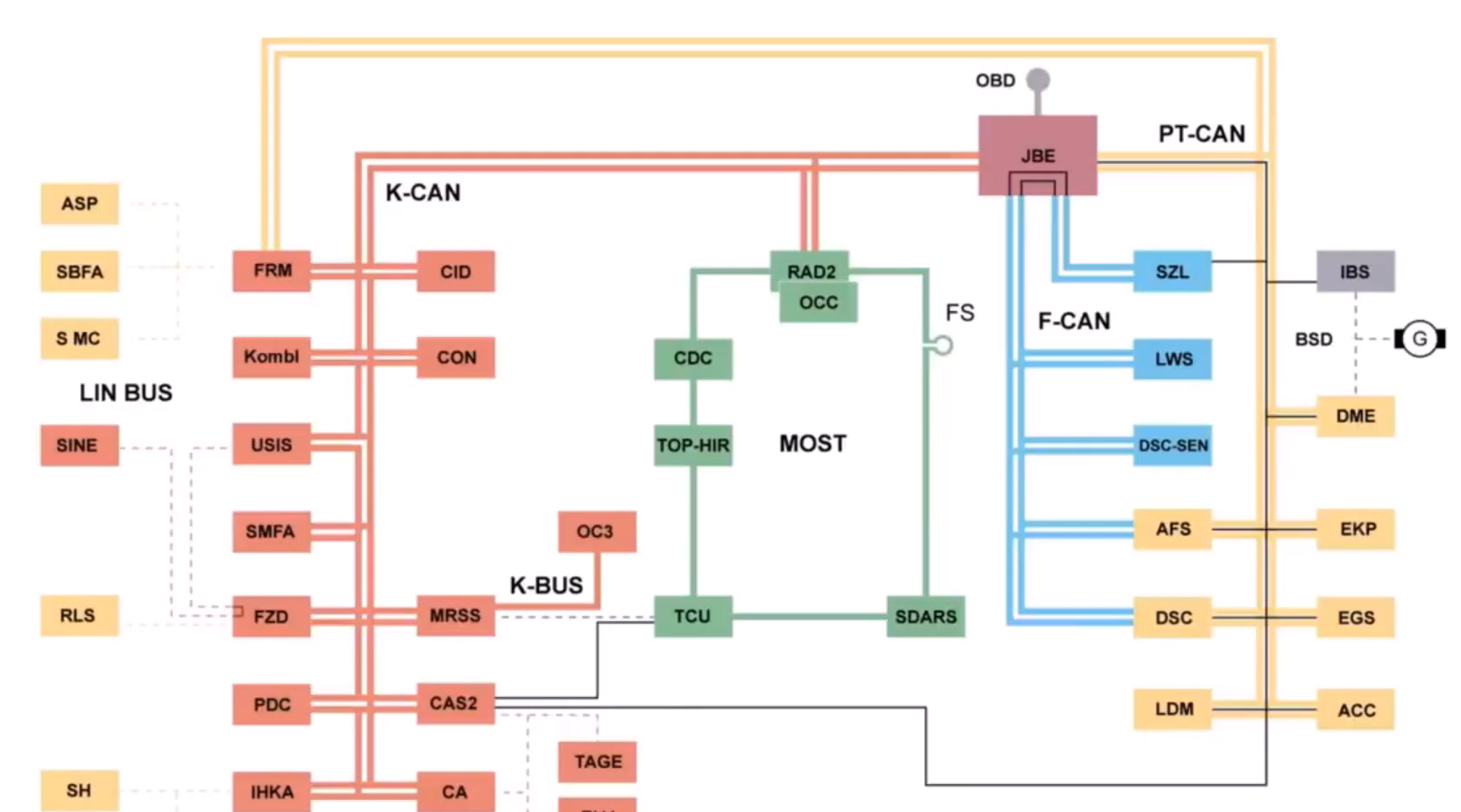
To effectively diagnose CAN Bus issues, you need to comprehend the network topology specific to your vehicle. Understanding the network topology is like knowing the road map of your car's communication system. Imagine your car's different parts, like the engine, transmission, and even the wipers, need to talk to each other, just like friends using different languages. These friends communicate through a special box in your car called the "gateway."
When you know this network map, you can perform "function tests" to check if everything is working as it should. For example, think about your car's speed. This information needs to travel from the wheel speed sensor, to ABS, then to various parts like the speedo, radio, the wipers, and more. The gateway helps translate this information into a language that each network understands.
So, sometimes, a test as simple as activating the turn signal indicator can give you feedback as to whether the CAN bus networks are communicating:
The Turn Signal Switch is on the Steering Column Module.
The Turn Signal message is sent on CAN Bus and shared to all networks via gateway.
The Body Control Module receives this message and activates the exterior lights.
The Instrument Cluster receives this message and displays the green indicator light..
Understanding the network map helps you know where to look and what to test, making it much easier to find and fix problems in your car's communication system.
Our CAN Bus and Network Diagnostics training course shows you how to map out your vehicle network to help make the most of vehicle function tests.
Find out more and join Diagnostic Coach here.

Understanding the network map is essential for CAN bus diagnostics.
Tip 2: Full OBD Scan
Performing a full OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) scan is a crucial step in CAN Bus diagnostics. It can quickly help identify if there are any network problems. If your scan tool can communicate with various modules, it's a good sign that the CAN network is likely functioning properly. However, if modules are missing or not responding, it might be an indication of a CAN Bus issue that needs further investigation.
It's essential to understand your vehicle's network topology and how it connects through the OBD connector. Some vehicles have all CAN networks ending at the OBD plug, which can be handy for testing. But in some cases, only one network is available through the OBD plug. If you can successfully communicate with all modules through the OBD, it indicates that the network connected to the OBD plug is probably in good shape.
However, when modules are missing or not responding, it's crucial to check power supplies, grounds, and fuses before diving into more complex CAN Bus network troubleshooting. This step helps rule out common electrical issues that might affect the network's operation.

A scan tool with ‘topology’ network view like this ThinkTool Master 2 is useful for network diagnostics.
Tip 3: Multimeter Checks
Before reaching for the oscilloscope, use a multimeter to perform some initial checks.
Importance of Multimeter Checks:
Resistance Check: Multimeter checks allow you to measure the resistance between the CAN High and CAN Low wires. The goal is to find a total resistance of 60 ohms, but this doesn't give you the complete picture of the network's health. It's more like checking the two ends of a bridge to make sure they're connected.
Continuity Check: You can also use the multimeter to test for continuity. This means ensuring that there's a good electrical path between points. You can check for continuity between ground, power supply, or even between the two wires in the CAN Bus network.
Voltage Check: Multimeters help you measure the voltage on the CAN lines. For a high speed CAN network, you'd typically see around 2.6V on CAN high and about 2.4V on CAN low. However, these values may vary depending on the number of modules and network activity. If the voltages on both CAN high and CAN low are the same, it could indicate a short circuit (which should have been confirmed by your resistance check). If both voltages are at 0V, it might suggest a short to ground. If the voltages don't look right, you could be dealing with an open circuit or a resistive short circuit.
How to Perform Multimeter Checks:
Resistance Check: Ensure the vehicle is asleep, or the battery is disconnected before performing this test. Set your multimeter to the resistance (ohms) mode. Connect the multimeter leads to the CAN high and CAN low wires. A total resistance of 60 ohms indicates a good connection. 120 ohms indicates a possible open circuit.
Continuity Check: Set your multimeter to the continuity mode (usually depicted by a sound wave or a diode symbol). Touch one lead to a point you want to test, like ground or power supply, and touch the other lead to the wire or connector you're testing. If the multimeter beeps or shows continuity, it means there's a good electrical path; this is a good sign for wires, but a bad sign when checking to ground or live.
Voltage Check: Ensure the vehicle is awake or have the ignition switched on. Set your multimeter to the DC voltage mode. Connect the positive (red) lead to CAN high and the negative (black) lead to CAN low. Measure the voltage and compare it to the expected values for your specific network. Around 2.6V on CAN high and about 2.4V on CAN low for High Speed CAN. Around 0.1V on CAN high and about 4.9V on CAN low for Low Speed CAN.
By using the multimeter for these checks, you can quickly identify basic issues such as open circuits, shorts, or abnormal resistances.
Our CAN Bus and Network Diagnostics training course shows you how to perform various multimeter network tests and accurately interpret the results and good and bad systems.
Find out more and join Diagnostic Coach here.

Performing multimeter checks helps you rule out common electrical problems in the CAN Bus network.
Tip 4: Oscilloscope Diagnosis
When you've confirmed a network issue and the basics are covered, it's time to bring out the oscilloscope. An oscilloscope provides a more in-depth analysis of the CAN Bus signals. Here's what it helps you achieve:
Visualizing CAN Bus Signals: CAN Bus communication involves electrical signals transmitted as voltage levels on the CAN high and CAN low wires. An oscilloscope allows you to visually represent these voltage signals over time. This visualization is crucial because it provides a clear and detailed view of how data is being transmitted and received on the network.
Identification of Faults: An oscilloscope can help you spot anomalies in the CAN Bus signals. It can reveal issues like short circuits, open circuits, voltage spikes, or noise in the network. By examining the waveform, you can identify irregularities which are essential for troubleshooting network issues.
Detection of Intermittent Faults: Many CAN Bus problems are intermittent, meaning they occur sporadically. Intermittent faults are often challenging to diagnose with other tools. The oscilloscope is invaluable for spotting intermittent faults that occur sporadically, helping you pinpoint the root causes.
Resistive Fault Detection: Sometimes, issues are related to resistive faults, such as high resistance in connectors or wires. An oscilloscope can reveal voltage drops or fluctuations that may indicate resistive problems in the network.
Differentiating High Speed and Low Speed Networks: CAN Bus networks can operate at different speeds. An oscilloscope enables you to distinguish between high speed and low speed networks by analyzing the waveform characteristics. This information is vital for diagnosing the correct part of the network.
Oscilloscope is a powerful diagnostic tool for CAN Bus issues, offering real-time visibility into the network's electrical signals. It helps you identify problems, locate faults, and ensure that the CAN Bus communication adheres to the required standards.
Our CAN Bus and Network Diagnostics training course shows you how to perform diagnostics with the oscilloscope with examples of good and bad networks and waveform downloads.
Find out more and join Diagnostic Coach here.

Mechanic Mindset Online Oscilloscope Training
Tip 5: Find and Isolate CAN Bus Faults
Diagnosing for a network issue is a process of elimination. Start by revisiting any available evidence, such as previous repair history, accident damage, or other work on the vehicle. This information can provide valuable clues for where to begin the diagnosis. If no specific leads are available, you may have to methodically test the network from one end of the car to the other, prioritizing the easiest access points.
The first step in the diagnostic process is to individually disconnect modules from the CAN bus network. This straightforward procedure can help identify if a specific module is responsible for the issue. It's a relatively simple test, though some modules might be challenging to access. If the problem persists even after disconnecting modules, it indicates a problem with the wiring. The next step involves locating connectors in the wiring loom, ideally a midpoint in the network, and disconnecting them to determine if the fault lies on one side of the car or the other. In cases where there aren’t any connectors, you might need to trace, cut, and repair wires. Some vehicles use splice points and non-standard joints that can be challenging to locate, so having the workshop data and wiring diagrams available is very important.
It’s important to cover the basics; a ‘complex’ issue causing various problems with wipers, speed indicators, and warning lights could be caused by a simple blown 5-amp ABS fuse. Hence, in CAN bus diagnostics, starting with the basics and systematically eliminating common issues is an essential approach to problem-solving.
The Diagnostic Coach subscription includes the FIXDIT Diagnostic Process training course that details a logical approach to all diagnostic work to find the faults fast and eliminate repeat repairs.
Find out more and join Diagnostic Coach here.

Mechanic Mindset FIXDIT Diagnosis Process course will help you diagnose CAN Bus faults faster
Sometimes the most complex issues have surprisingly simple solutions. Always start by checking the basics, like fuses and connectors, as these can often be the source of CAN Bus problems. And don't forget to document your findings, as this can help you track down and resolve issues more efficiently.
By following these five tips and staying persistent in your diagnostic efforts, you can become proficient in CAN Bus diagnostics. It's a journey of continuous learning, and with practice, you'll master this complex network and its quirks. Happy diagnosing!
